User Manual for Music Mixer 5
Effects Menu Functions
- Equalizer
-
This function allows you to individually amplify or attenuate low, mid, or high-frequency bands. It applies to the selected data from the current file. The equalizer has 9 frequency bands (from 32 Hz (bass) to 16 KHz (treble)). You can define the level of each frequency band with the knobs or by directly entering the values in the corresponding fields.
- Echo
-
This function applies an "Echo" effect. It applies to the selected data from the current file. You can define the shape of the echo by setting the time elapsed between each repetition of the original sound and how this echo will decrease with the knobs or by directly entering the values in the corresponding fields.
Level (from 0 to 10): This parameter determines the volume of the repetitions. If this parameter is set to 0, the volume decreases by half with each repetition, and the echo "fades out" quickly. If this parameter is set to 10, the echo has a constant volume equal to the volume of the original signal.
Delay (from 0 to 1000 ms): This parameter determines the number of milliseconds between each repetition.
- Reverb
-
This function applies a reverb effect, as if the sound were played in a room. It applies to the selected data from the current file. In practice, the "Reverb" effect simulates the reflection of sound on the walls of the room by adding multiple short echoes to the original sound. You can define the shape of the reverberation by specifying the delay and amplitude of the repetitions of the original sound with the knobs or by directly entering the values in the corresponding fields.
Level (from 0 to 10): This parameter determines the power of the echoes. The higher the value of this parameter, the more the sound will seem to be played in a room with reflective walls; conversely, the smaller the value, the more the sound will seem to be played in a room that "muffles" the sound.
Delay (from 0 to 1000 ms): This parameter determines the number of milliseconds between each echo. The longer the delay, the more the sound will seem to be played in a spacious room; conversely, the shorter the delay, the more the sound will seem to be played in a cramped room.
- Tremolo
-
This function applies a tremolo effect. It applies to the selected data from the current file. In practice, the "Tremolo" effect rapidly alternates increasing and decreasing the volume. You can define the shape of this tremolo by setting the frequency and amplitude of the variations with the knobs or by directly entering the values in the corresponding fields. You can also choose whether these variations should follow a linear or sinusoidal function.
Amplitude (from 0 to 10): This parameter determines the "depth" of the variations.
Frequency (from 0 to 100): This parameter determines the number of variations per second (i.e., the number of times the volume will be successively increased and then decreased in one second).
- Phaser
-
This function applies a "Phaser" effect. It applies to the selected data from the current file. This effect copies the waveform of the original sound, reverses it (out of phase), and then adds it to the original sound with a determined delay.
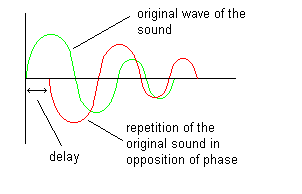
You can set the delay time with the knob or by directly entering the value in the corresponding field.
Delay (from 1 to 100 samples): This parameter determines the delay of the repetition, measured in number of samples for more precision. For a short delay, the effect will produce a reduction in sound; the sound seems less "bright." For a long delay, it will, on the contrary, produce a slight amplification; the sound seems more "heavy."
The corresponding value in seconds can be found by: Delay Time = Number of Delayed Samples / Sample Frequency
- Distortion
-
This function applies a distortion effect to the sound (for example, to simulate the effect of a saturated amplifier, an effect often used for guitar sounds). It applies to the selected data from the current file. In practice, this effect modifies the sound when the volume is above a certain threshold (called "distortion threshold") to a unique value defined as the "attachment level." If the volume is below the threshold, the sound is not modified. You can define the "distortion threshold" and the "attachment level" with the knobs or by directly entering the values in the corresponding fields.
- Noise Gate
-
This function applies a "Noise Gate" effect to the sound. It applies to the selected data from the current file. It allows you to eliminate the weakest sounds, letting only the strongest sounds pass through. In practice, this effect erases the sound when the volume is below a certain threshold. If the volume is above the threshold, the sound is not modified. You can define this threshold with the knob or by directly entering the value in the corresponding field.